Four questions about the debt ceiling crisis of the US government
It has been four months since the US government debt reached the legal ceiling of $31.4 trillion, and the cash surplus on hand of the US Treasury has plummeted recently, which has aggravated the concerns about the default of US government debt. According to the deadline warned by Finance Minister Yellen — — That is, on June 1, the US debt default has entered a "countdown".
So, what is the US government debt ceiling? Once there is a debt default, what will be the impact?
Question 1: What is the debt ceiling of the US government?
The US Treasury Department is responsible for the income and expenditure of the US federal government, and the income mainly comes from two aspects: tax revenue and debt income; Expenditure includes personnel salary expenditure, various project expenditures and repayment of due debts and interest.
The "debt ceiling" is the maximum amount of debt set by the US Congress for the federal government, which can be understood as the "credit card limit" of the US Treasury.
Question 2: What is the debt ceiling of the US government?
Since 1960, the United States has raised the debt ceiling 78 times, with an average increase every nine months. In 1981, when then US President Ronald Reagan took office, Congress raised the debt ceiling to $1 trillion for the first time.

At that time, US President Ronald ReaganIn the past decade, the so-called temporary increase in the debt ceiling has appeared 21 times. Now I have to ask for raising the debt ceiling again, otherwise the government will not be able to operate after mid-February.
Since then, the scale of US government debt has been expanding, rising from about $3.2 trillion in 1990 to about $27.74 trillion in 2020. The debt ceiling authorized by the US Congress has also been continuously raised. On January 19, 2023, the US government debt hit the ceiling of about $31.4 trillion. The US Treasury can only take some "unconventional measures" to make ends meet.
Question 3: What are the two parties arguing about the government debt ceiling?
In the context of deepening political polarization, the debt ceiling has increasingly become a battlefield for party struggle. American politicians use the debt ceiling as a bargaining chip and threaten to default on their debts to coerce the other side into making concessions on certain issues.
On April 26th, the US House of Representatives passed a bill proposed by the Republican Party, demanding that the government cut the federal fiscal expenditure by 4.5 trillion US dollars in the next 10 years and cancel some clean energy tax cuts. On this premise, Congress will approve raising the debt ceiling by $1.5 trillion. US President Biden and the Democratic Party want to raise the debt ceiling unconditionally.
Democrat Schumer, the majority leader of the Senate, accused the Republican Party of pushing the United States into debt default.
Senate Majority Leader, Democrat Chuck SchumerThis bill can be called "American Default Act", and that’s the truth — — American Default Act.
On the other hand, the Republican Party accused the Biden administration of being the chief culprit in the risk of debt default.
House Majority Leader, Republican Steve ScalisePresident Biden maxed out the country’s credit card.
Question 4: If the U.S. government defaults on its debts, what will be the impact?
Economists in the United States agree that if the government defaults on its debt for more than six weeks, not only will the stock market be severely hit, but the American economy will also decline, with an overall decline of more than 4%, which will lead to the loss of 8 million jobs and the unemployment rate will soar to more than 8%.
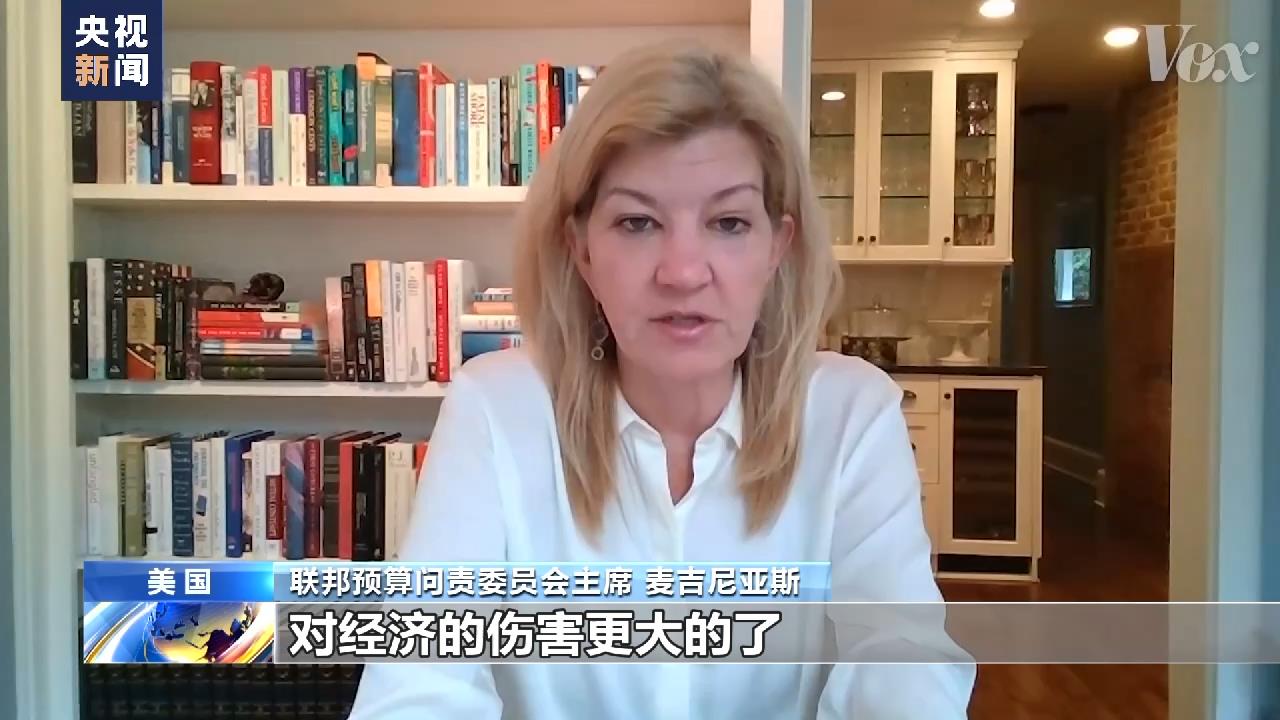
Michael geaneas, Chairman of the Federal Budget Accountability Committee.Nothing hurts the economy more than the default of government debt.
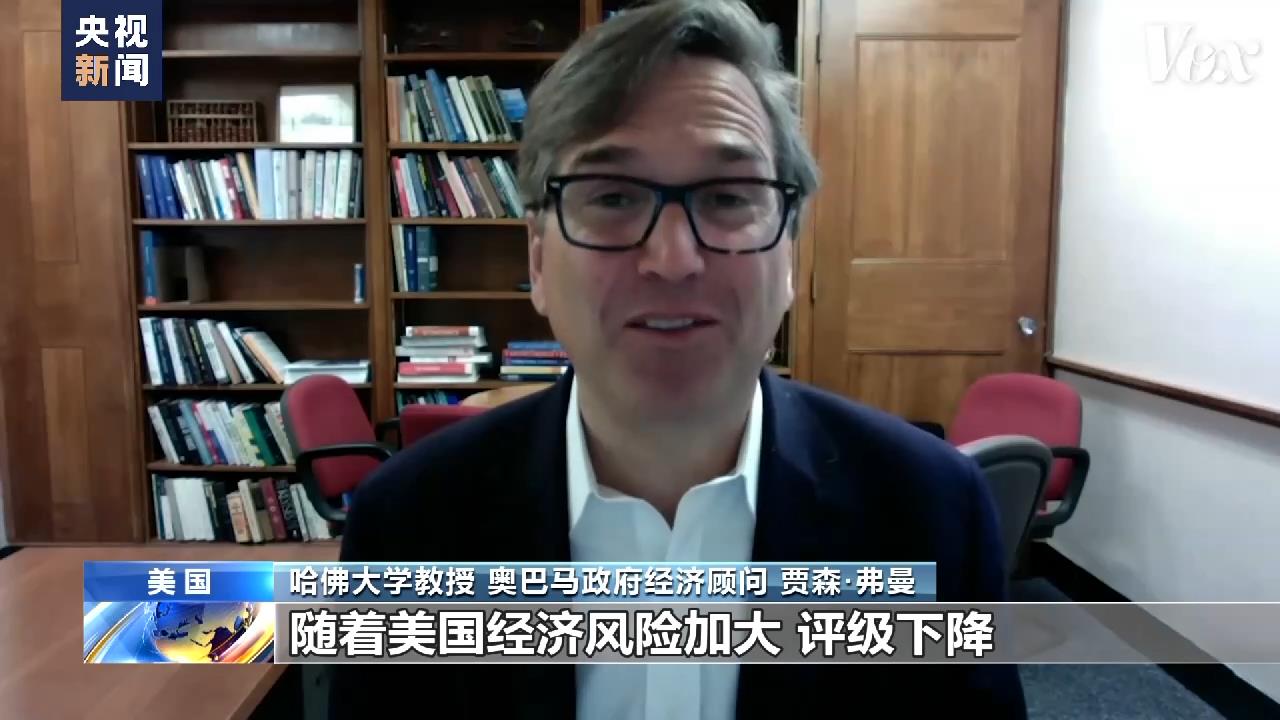
Jason Furman, a professor at Harvard University and an economic adviser to the Obama administration: As the economic risks in the United States increase and the rating declines, interest rates will also soar. When the interest rate of government bonds rises, other interest rates will also rise.
The increase in interest rates on credit cards, car loans and mortgage loans means that the monthly repayment amount of ordinary people will increase significantly. The distribution of pension and medical insurance funds, which account for the bulk of fiscal expenditure, will also be delayed, which will seriously hurt low-and middle-income people.
Although from past experience, the two parties will be forced to reach some kind of compromise at the last minute under various pressures. However, the frequent occurrence of the "debt ceiling" crisis will continue to consume the value of US dollar assets such as US government credit and US debt, and trigger a crisis of confidence in the US dollar and US Treasury bonds in the global market, thus bringing a significant impact and far-reaching impact on the global economic structure.
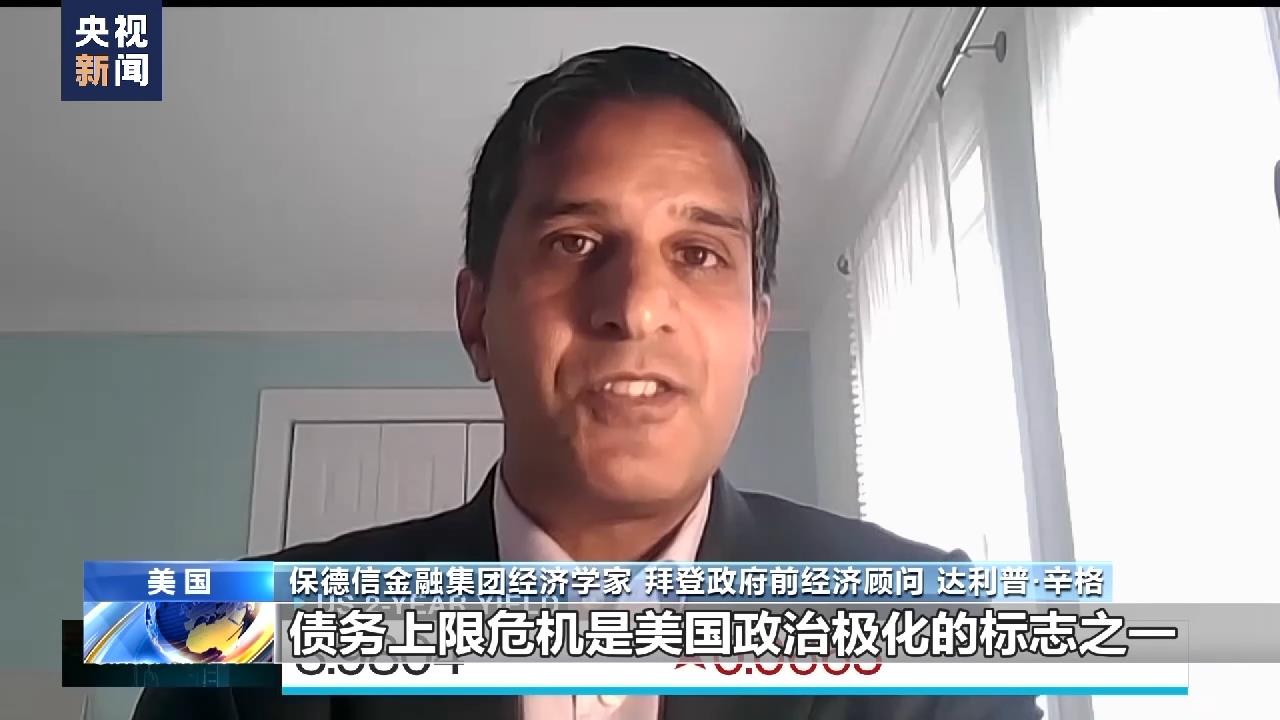
Dalip Singh, economist of Prudential Financial Group and former economic adviser of Biden administration.The debt ceiling crisis is one of the signs of political polarization in the United States. Other important economies will not default, and they will not even discuss or consider default. Dollar hegemony is just a network based on trust, and we are pushing ourselves to a dangerous situation and getting closer and closer to debt default. This is very dangerous and costly.